Google Cloud Functions
When Does Cold Start Happen on Google Cloud Functions?
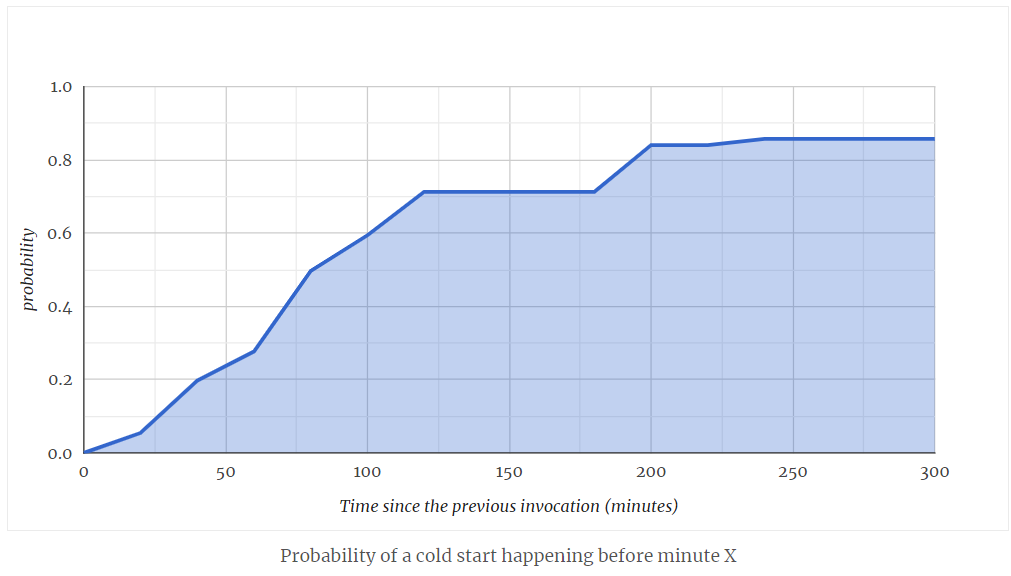
The very first cold start happens when the very first request comes in after deployment.
After that request is processed, the instance stays alive for the time being to be reused for subsequent requests. But for how long?
Read more...Google Cloud Functions: Cold Start Duration per Language
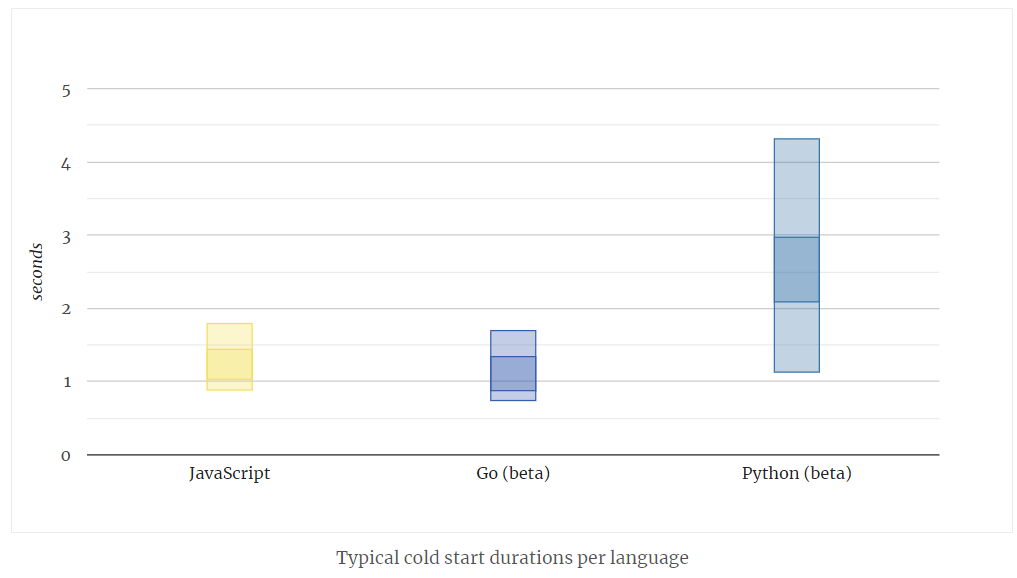
The following chart shows the typical range of cold starts in Google Cloud Functions, broken down per language. The darker ranges are the most common 67% of durations, and lighter ranges include 95%.
Read more...Google Cloud Functions: Cold Start Duration per Instance Size
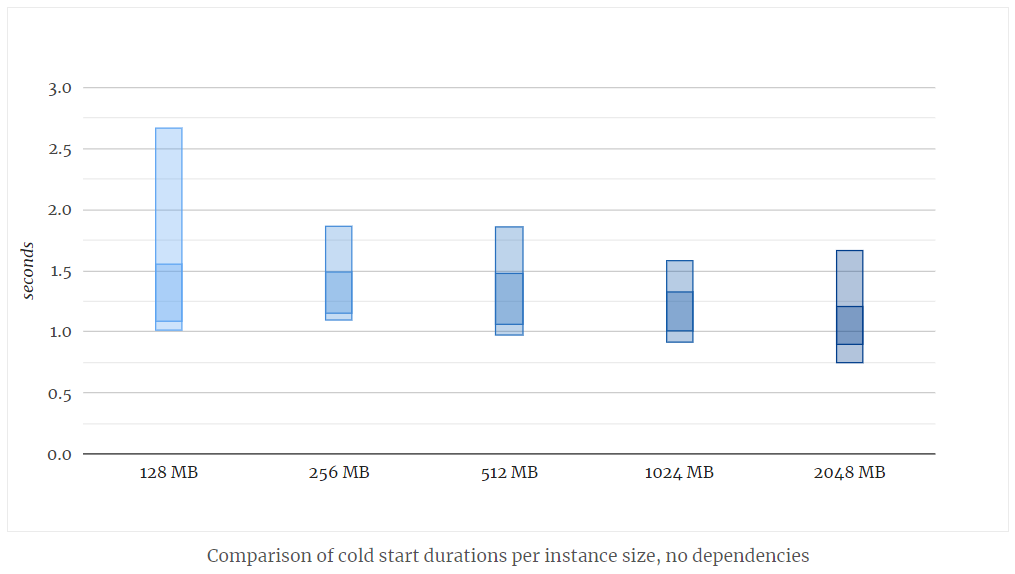
Google Cloud Functions have a setting to define the memory size that gets allocated to a single instance of a function. The CPU resources are allocated proportionally to the memory. So, in theory, larger instances could start faster.
Read more...