Performance
Choosing the Number of Shards in Temporal History Service
Tuning the sharding configuration for the optimal cluster performance with the numHistoryShards config.
Read more...Maru: Load Testing Tool for Temporal Workflows
Benchmarking Temporal deployments with a simple load simulator tool
Read more...Load-Testing Azure Functions with Loader.io
Verifying your Function App as a valid target for the cloud load testing.
Read more...Serverless at Scale: Serving StackOverflow-like Traffic
Scalability test for HTTP-triggered serverless functions across AWS, Azure and GCP
Read more...From 0 to 1000 Instances: How Serverless Providers Scale Queue Processing
Comparison of queue processing scalability for FaaS across AWS, Azure and GCP
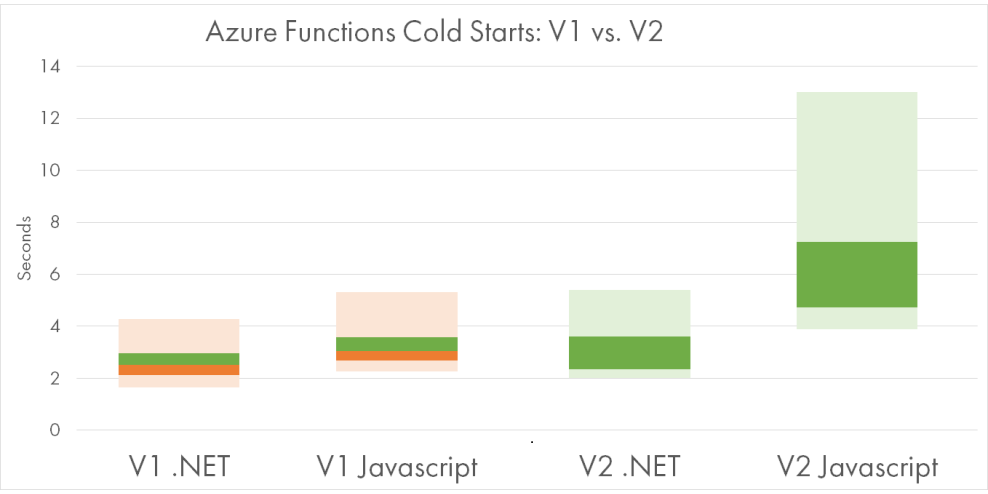
Read more...Azure Functions V2 Is Released, How Performant Is It?
Comparison of performance benchmarks for Azure Functions V1 and V2
Read more...Serverless: Cold Start War
Comparison of cold start statistics for FaaS across AWS, Azure and GCP
Read more...Cold Starts Beyond First Request in Azure Functions
Can we avoid cold starts by keeping Functions warm, and will cold starts occur on scale out? Let's try!
Read more...Azure Functions: Cold Starts in Numbers
Auto-provisioning and auto-scalability are the killer features of Function-as-a-Service cloud offerings, and Azure Functions in particular.
One drawback of such dynamic provisioning is a phenomenon called “Cold Start”. Basically, applications that haven’t been used for a while take longer to startup and to handle the first request.
Read more...Load Testing Azure SQL Database by Copying Traffic from Production SQL Server
Azure SQL Database is a managed service that provides low-maintenance SQL Server instances in the cloud. You don’t have to run and update VMs, or even take backups and setup failover clusters. Microsoft will do administration for you, you just pay an hourly fee.
Read more...Event Sourcing: Optimizing NEventStore SQL read performance
In my previous post about Event Store read complexity I described how the growth of reads from the event database might be quadratic in respect to amount of events per aggregate.
Read more...